Difference between revisions of "Relays"
(revert to 03:07, 15 May 2006 by 65.28.98.207) |
(linkify to article that goes into more detail) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:Main-G5Q-14.jpg|Relay]] | [[Image:Main-G5Q-14.jpg|Relay]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | {{mergeto|switches}} | |
| + | |||
| + | === Description === | ||
| + | A PIC can't source more than 25mA, so how do I turn on/off a light bulb? With a relay! | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PIC can't source more than 25mA, so how do I turn on/off a relay? With a transistor! | ||
Relays are those large black boxes that go 'click'. There is a coil inside. When current flows through the coil a magnetic field causes the the internal paddle to move postions. This paddle usually carrys large currents or large voltages. | Relays are those large black boxes that go 'click'. There is a coil inside. When current flows through the coil a magnetic field causes the the internal paddle to move postions. This paddle usually carrys large currents or large voltages. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 19: | ||
There are many configurations based on the circuit you need to control. DPDT (double pull double throw), SPDT (single pull double throw) are two of the most common. View the equivalent circuits in the mfg's datasheets to get an idea of how they work. | There are many configurations based on the circuit you need to control. DPDT (double pull double throw), SPDT (single pull double throw) are two of the most common. View the equivalent circuits in the mfg's datasheets to get an idea of how they work. | ||
| − | + | === Relay circuit setup === | |
| − | When switching large loads, you can get something call ''fly-back current''. | + | |
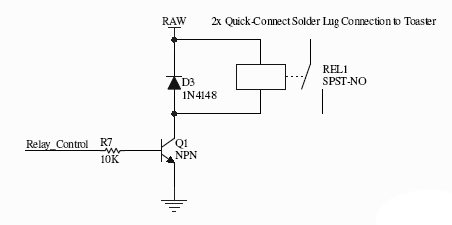
| + | Many microcontrollers cannot source enough current to feed the control coil. So Q1 is any old BJT (2N3904 is a good one) to turn on/off the relay. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When switching large loads, you can get something call ''fly-back current''. The fly-back current can cause surges of voltage when a device is kicked on/off (imagine when the lights dim when you turn on the microwave). | ||
| + | These surges can arc and destroy nearby components. | ||
[[Image:Relay-Example.jpg|Example Relay Circuit]] | [[Image:Relay-Example.jpg|Example Relay Circuit]] | ||
| − | + | The diode 1N4148 (simple, cheap, can handle ~200mA current) is there to direct the fly-back current to a safe path. Without that diode, the flyback current could arc and destroy some nearby component. | |
| + | Be sure to watch how you polarize your diode. | ||
| − | + | === Documents === | |
| + | |||
| + | === Footprints === | ||
| − | |||
[[SFE_Footprint_Library|SFE Footprint Library]] | [[SFE_Footprint_Library|SFE Footprint Library]] | ||
There are various footprints available. Always be sure to do a 1:1 printout of your board and matchup the physical relay to the printout before PCB fab. Sometime the manufacturers list recommended footprints from the bottom view which can lead to mirrored and incorrect FPs. | There are various footprints available. Always be sure to do a 1:1 printout of your board and matchup the physical relay to the printout before PCB fab. Sometime the manufacturers list recommended footprints from the bottom view which can lead to mirrored and incorrect FPs. | ||
| − | + | === Manufacturer Info === | |
| + | |||
| + | === Supplier Info === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''(Is there anything special about these particular relays?)'' | ||
| − | |||
Digikey part # : G5Q-1-DC12<br> | Digikey part # : G5Q-1-DC12<br> | ||
| − | Single Piece Price : $2.25 | + | Single Piece Price : $2.25<br> |
| + | 12 VDC SPDT | ||
| + | |||
| + | All Electronics part # : [http://www.allelectronics.com/make-a-store/item/RLY-275/24-VDC-SPDT-PC-MOUNT-POWER-RELAY/-/1.html RLY-275]<br> | ||
| + | Single Piece Price: $0.50<br> | ||
| + | 24 VDC SPDT | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Related Items === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Further Reading === | ||
| − | + | * [[Switch Terminology]] | |
| + | * [[Basic_Circuits_and_Circuit_Building_Blocks#Relay_with_Diode_Snubber | Relay with Diode Snubber]] | ||
| + | * [[Basic_Circuits_and_Circuit_Building_Blocks#Transistor_Low_Side_Switch]] | ||
| + | * [[relay CPU]] | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/flyback_diode Wikipedia: flyback diode] | ||
| + | * [http://www.dnatechindia.com/index.php/Tutorials/8051-Tutorial/Relay-Interfacing.html Interfacing Relay To Micro controller] | ||
[[Category:Components]] | [[Category:Components]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:24, 29 January 2024
It has been suggested that this page or section be merged into [[::switches|switches]]. (Discuss)
Contents
Description
A PIC can't source more than 25mA, so how do I turn on/off a light bulb? With a relay!
A PIC can't source more than 25mA, so how do I turn on/off a relay? With a transistor!
Relays are those large black boxes that go 'click'. There is a coil inside. When current flows through the coil a magnetic field causes the the internal paddle to move postions. This paddle usually carrys large currents or large voltages.
Most relays have various ratings. We'll start with the coil voltage. '12VDC' for example means that the control coil requires 12V DC for the unit to switch the paddle. The other rating you'll see is '10A'. This refers to the amount of current you can run through the control paddle contact (not the current through the coil). So a 10A relay can handle a load of up to 10A- less than 10A is no problem. What happens if you try to run more current than the max? Well, it will probably work, but at higher currents the internal sparking will tend to burn the contacts. The paddle can potentially spot-weld itself to the contacts in extreme cases.
There are sealed and vented relays. Vented relays tend to run a bit cooler, but are more suceptible to gunk getting into the moving parts.
There are many configurations based on the circuit you need to control. DPDT (double pull double throw), SPDT (single pull double throw) are two of the most common. View the equivalent circuits in the mfg's datasheets to get an idea of how they work.
Relay circuit setup
Many microcontrollers cannot source enough current to feed the control coil. So Q1 is any old BJT (2N3904 is a good one) to turn on/off the relay.
When switching large loads, you can get something call fly-back current. The fly-back current can cause surges of voltage when a device is kicked on/off (imagine when the lights dim when you turn on the microwave). These surges can arc and destroy nearby components.
The diode 1N4148 (simple, cheap, can handle ~200mA current) is there to direct the fly-back current to a safe path. Without that diode, the flyback current could arc and destroy some nearby component. Be sure to watch how you polarize your diode.
Documents
Footprints
There are various footprints available. Always be sure to do a 1:1 printout of your board and matchup the physical relay to the printout before PCB fab. Sometime the manufacturers list recommended footprints from the bottom view which can lead to mirrored and incorrect FPs.
Manufacturer Info
Supplier Info
(Is there anything special about these particular relays?)
Digikey part # : G5Q-1-DC12
Single Piece Price : $2.25
12 VDC SPDT
All Electronics part # : RLY-275
Single Piece Price: $0.50
24 VDC SPDT