Difference between revisions of "DsPIC30F 5011 Development Board"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
**[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70165E.pdf dsPIC33F Family Data Sheet] | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70165E.pdf dsPIC33F Family Data Sheet] | ||
**[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/80279B.pdf dsPIC33F Rev. A2 Silicon Errata] | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/80279B.pdf dsPIC33F Rev. A2 Silicon Errata] | ||
| − | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/ | + | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/80306E.pdf dsPIC33FJXXXGPX06/X08/X10 Rev. A2/A3/A4 Silicon Errata] |
**[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70152C.pdf Flash Programming Specification] | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70152C.pdf Flash Programming Specification] | ||
**[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70172A.pdf dsPIC30F to dsPIC33F Conversion Guidelines] | **[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70172A.pdf dsPIC30F to dsPIC33F Conversion Guidelines] | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 4 December 2008
Contents
Introduction
Features of dsPIC30F5011
- 2.5 to 5V
- Up to 30MIPs
- High current/sink source I/O pins: 25mA
- DSP Instruction Set
- Dual programming techniques: ICSP and RTSP
- UART: up to 2 modules
- I2C: up to 1Mbps
- 10-bit A/D, 1.1 Msps
- 12-bit A/D, 200 ksps
- 44K flash (66Kb), 4Kb RAM, 1Kb EEPROM
- No DAC
- Pin-to-pin compatible with other dsPICs
| dsPic | Price US$ |
MIPs | Flash (kB) |
RAM (kB) |
EEPROM (kB) |
I/O | ADC 12-bit |
IC | OC | Motor Ctrl |
Timers | QEI | UART | SPI | I2C | CAN | Codec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30F5011 | 5.91 | 30 | 66 | 4 | 1 | 52 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 5x16bit 2x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 30F6011A | 7.73 | 30 | 132 | 6 | 2 | 52 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 5x16bit 2x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 30F6012A | 7.85 | 30 | 144 | 8 | 4 | 52 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 5x16bit 2x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP206 | 4.62 | 40 | 128 | 8 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP306 | 4.81 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP706 | 5.49 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 33FJ128MC506 | 4.97 | 40 | 128 | 8 | 0 | 53 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 33FJ128MC706 | 5.38 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 33FJ256GP506 | 6.11 | 40 | 256 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
Web Page
Forum
- Microchip: Official forum by Microchip
- MPLAB ICD 2: Subforum on ICD 2 programmer
- MPLAB IDE: Subforum on IDE
- MPLAB C30 Compiler, ASM30, Link30 forum: Subforum on C compiler. Refer to MPLAB C30 C Compiler User's Guide Chapter 3
- dsPIC30F Topics: Subformum on dsPIC30F
- GNUPIC: Discussion on PIC in Linux Systems
- HI-TECH Software Forum: Discussion on dsPICC, a C compiler developed by HI-TECH
- PICList: Discussion on older PIC systems (not dsPIC)
- PicKit: Discussion on PICkit/PICkit 2 programmers
- FreeRTOS Real Time Kernel: Open Discussion and Support on FreeRTOS
- Nabble: MicroControllers - GNUPIC
References
- dsPIC30F
- dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual Sections: Contains detailed descriptions on dsPIC30F register definitions and example codes
- dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual Errata (Use with revision 70046B only)
- dsPIC30F5011, dsPIC30F5013 Data Sheet
- dsPIC30F5011/5013 Rev. A1/A2 Silicon Errata
- dsPIC30F5011/5013 Rev. A3 Silicon Errata
- Flash Programming Specification
- dsPIC30F Programmer's Reference Manual
- dsPIC30F Programmer's Reference Manual Errata (use with revision DS70030E only)
- dsPIC33F
- ICD2 Programmer
- MPLAB
- C30 Compiler
- MPLAB C30 C Compiler User's Guide: Contains commands for using pic30-elf-gcc
- 16-bit Language Tools Libraries: Contains summaries and examples of using DSP libraries, standard C libraries and device libraries
- MPLAB ASM30, MPLAB LINK30 and Utilities User's Guide
- dsPIC30F Language Tools Quick Reference Card
Code Examples
Related Development
Programming Methods
- There are 2 programming methods: In-Circuit Serial Programming (ICSP) and Run-Time Self-Programming (RTSP)
- ICSP allows the devices to be programmed after being placed in a circuit board.
- RTSP allows the devices to be programmed when an embedded program is already in operation.
ICSP: External Programmer (ICD2)
- Two types of ICSP are available: ICSP and Enhanced ICSP. Both of them require setting MCLR# to VIHH (9V – 13.25V).
- Standard ICSP
- Use external programmer (e.g. MPLAB® ICD 2, MPLAB® PM3 or PRO MATE® II) only.
- Required low-level programming to erase, program and verify the chip.
- Slower, because codes are serially executed.
- Program memory can be erased using Normal-Voltage (4.5 – 5.5V) or Low-Voltage (2.5V – 4.5V).
- Enhanced ICSP
- Use external programmer and Programming Executive (PE).
- PE is stored in the on-chip memory.
- PE allows faster programming.
- PE can be downloaded to the chip by external programmer using the standard ICSP method.
- PE contains a small command set to erase, program and verify the chip, avoiding the need of low-level programming.
Hardware Interface
| Pin Label | Function | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| MCLR# | Programming Enable | 7 |
| VDD | Power Supply | 10, 26, 38, 57 |
| VSS | Ground | 9, 25, 41, 56 |
| PGC | Serial Clock | 17 |
| PGD | Serial Data | 18 |
| Product Name | Interface with PC | Interface with Device | Price (US) | Postage (US) | Total (US) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPLAB® ICD 2 | USB or RS232 | 6-PIN RJ-12 connector | $159.99 | - | - |
| Full Speed USB Microchip ICD2 Debugger and Programmer |
USB | 6-PIN ICSP connector 6-PIN RJ-12 connector |
$72.00 | $12.00 | $84.00 |
| Mini Microchip Compatible ICD2 Debugger and Programmer |
RS232 | 6-PIN ICSP connector 6-PIN RJ-12 connector |
$45.00 | $10.00 | $55.00 |
| ICDX30 | RS232 | 6-pin RJ-11 | $51.00 | $47.46 | $98.46 |
| *Clone Microchip ICD2 (Now Using) | USB | 6-pin flat cables | $30.00 | $12.00 | $42.00 |
| Source | Schematic | PIC16F877A Bootloader |
|---|---|---|
| Patrick Touzet | Yes | HEX |
| Nebadje | Yes | Zip |
Software Interface
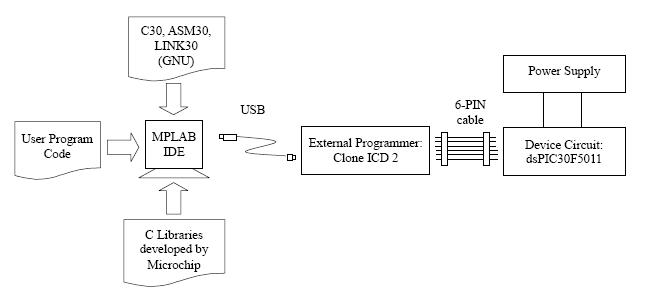
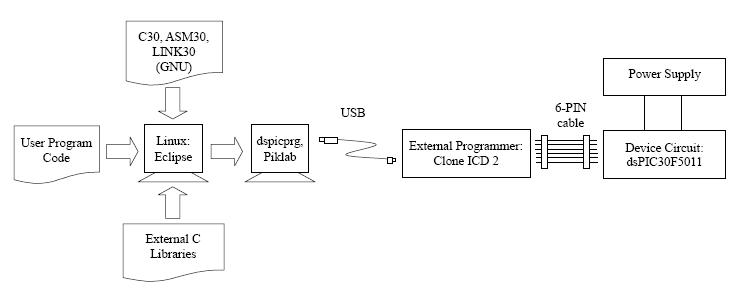
- The program can be written and compiled in an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) using either Assembly or C. The complied codes are then loaded to the device through the external programmer.
| Product Name | Features | OS | Price (US$) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPLAB® IDE | Assembler Only | Windows | Free |
| MPLAB® C30 | Assembler and C-Compiler | Windows | $895.00 (Free student version1) |
| Piklab | Assembler and C-Compiler | Linux | Free |
- Full-featured for the first 60 days. After 60 days, some code optimization functions are disabled. The compiler will continue to function after 60 days, but code size may increase.
RTSP: COM Port (Bootloader)
- RTSP works in normal voltage (MCLR# no need to raise to VIHH).
- No literature has mentioned the incorporation of Programming Executive (PE). Presumably, since Enhanced ICSP needs to set MCLR# to VIHH, RTSP cannot use PE.
- Refer to bootloader section.
IC Requirements
| Part No. | Description | Min Temp | Max Temp | Min Volt | Max Volt | Typ Cur | Max Cur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dsPIC30F5011-30I/PT | uP | -40oC | 85oC | 2.5V [1] | 5.5V | 145mA | 217mA |
| MAX3232ESE | RS232 driver | -40oC | 85oC | 3.0V | 5.5V | 0.3mA | 1.0mA |
| DS3695N | RS485 driver | -40oC | 85oC | 4.75V | 5.25V | 42mA | 60mA |
| DAC6574IDGS | 10-bit Quad-DAC I2C | -40oC | 105oC | 2.7V | 5.5V | 0.6mA | 0.9mA |
| 74HC14D | Quad-Schmitt Trigger | -40oC | 125oC | 2.0V | 6.0V | 0.02mA | |
| Overall | -40oC | 85oC | 4.75V | 5.25V | <300mA [2] | ||
| dsPIC33FJ128GP306-I/PT | uP | -40oC | 85oC | 3.0V [1] | 3.6V | 74mA | 250mA |
| ADM3485EARZ | RS485 driver | -40oC | 85oC | 3.0V | 3.6V | 1.1mA | 2.2mA |
| 24LC256-I/SN | 256kBits I2C EEPROM | -40oC | 85oC | 2.5V | 5.5V | 400uA | 3mA |
| LM3940IMP-3.3 | 5V-3.3V Regulator | -40oC | 125oC | 5.0V | 7.5V | 10mA | 250mA |
- Minimum voltage measured is 3.3V (with 2 LEDs blinking) running at 30MHz.
- Measured current at 5V is 180mA (with 2 LEDs blinking only)
Development Environment
Windows
- C-Compiler, Assembler and Linker are under GNU license.
- MPLAB C30 C Compiler (*.c -> *.s)
- MPLAB ASM30 Assembler (*.s -> *.o)
- MPLAB LINK30 Linker (*.o -> *.bin)
- PA optimizer, simulator, runtime libraries, header files, include files, and linker scripts are not covered by GNU. Reference is here.
- Microchip has integrated ASM30, LINK30, assembly header files, linker scripts in MPLAB IDE, which is free for download.
- MPLAB C30 costs US$895. A 60-day free student version is also available. After 60-days, the optimizer is automatically disabled, while other tools can still function properly. Refer to Table 2.4.
- C-libraries contained in C30 includes (Refer to 16-Bit Language Tools Libraries from Microchip).
| Library | Directory (\\Microchip\MPLAB C30) |
Major functions |
|---|---|---|
| DSP Library (e.g. libdsp-coff.a) |
\lib \src\dsp \support\h |
Vector, Matrix, Filter, etc. |
| 16-Bit Peripheral Libraries (e.g. libp30F5011-coff.a) |
\lib \src\peripheral \support\h |
ADC12, IOPort, UART, I2C, etc. |
| Standard C Libraries (e.g. libc-coff.a, libm-coff.a, libpic-coff.a) |
\lib \src\libm \include |
stdio.h, time.h, float.h, math.h, |
| MPLAB C30 Built-in Functions | none | _buildin_addab, _buildin_add, _buildinmpy, etc |
Linux
- C Compiler, Assembler and Linker are under GNU license.
- The code can be downloaded from Microchip at here.
- Current MPLAB ASM30 Assembler: v2.04
- Current MPLAB C30 Compiler: v2.04
- John Steele Scott has made templates that can be readily used by Debian-based systems.
- For v1.32, the necessary conversion to *.deb has been done already at here.
- Download pic30-1.32-debian.tar.bz2 for Template v1.32.
- Download pic30-binutils_1.32-1_i386.deb for the assember.
- Download pic30-gcc_1.32-1_i386.deb for the compiler.
- For v2.00
- goto http://www.baycom.org/~tom/dspic/
- download pic30-gcc-2.00-1.i386.rpm and pic30-binutils-2.00-1.i386.rpm
- convert to deb files
- install these two deb files
- For v3.01, convert the Toolchain following instructions at here
- Pre-install these packages: dpkg-dev, debhelper, bison, flex, sysutils, gcc-3.3, fakeroot
- cmd: sudo apt-get install dpkg-dev debhelper bison flex sysutils gcc-3.3 fakeroot
- Download and unzip template: pic30-3.01.tar.bz2
- Download assembler: mplabalc30v3_01_A.tar.gz. Save under /pic30-3.01/pic30-binutils-3.01/upstream/
- Download c-compiler: mplabc30v3_01_A.tgz. Save under /pic30-3.01/pic30-gcc-3.01/upstream/
- Install MPLAB_C30_v3_01-StudentEdition under Windows
- Copy directories /include, /lib, /support, and /bin/c30_device.info to pic30-3.01/pic30-support-3.01/upstream/
- Pack pic30-binutils into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-binutils-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- Pack pic30-gcc-3.01 into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-gcc-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- Pack pic30-gcc-3.01 into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-support-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- install pic30-binutils_3.01-1_i386.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-binutils_3.01-1_i386.deb
- install pic30-gcc_3.01-1_i386.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-gcc_3.01-1_i386.deb
- install pic30-support_3.01-1_all.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-support_3.01-1_all.deb
- Pre-install these packages: dpkg-dev, debhelper, bison, flex, sysutils, gcc-3.3, fakeroot
- Important Note: Only the compiler is free. The header files and library are owned by Microchip.
- Thomas Sailer suggested to download the Student version of C30 compiler and then build the libraries without source code. A package template for Fedora system is available here.
- Instructions for filling the upstream direction is available here.
- Alteratively, Stephan Walter has started a project to develop C Runtime Library for dsPIC.
- Current libraries in version 0.1.1 include: assert.h, cdefs.h, ctype.h, errno.h, inttypes.h, stdint.h, stdio.h, stdlib.h, string.h
- Burning Program Codes to Target Board
- Use 'dspicprg and dspicdmp' utilities developed by Homer Reid to burn hex code (*.hex) to devices. See Reference here. Through serial port only?
- Use Piklab IDE. Details on file format not known.
- Use MPLAB IDE to burn hex code (*.hex) to devices.
Code Optimization
- Below is a comparsion between different optimization levels for the project including drivers for 2 projects.
| Optimization | Description | Project 1 Code Size (byte) |
Project 1 Data Usage (byte) |
Project 2 Code Size (byte) |
Project 2 Data Usage (byte) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O0 | No optimization Fastest Compilation |
6222 (9%) | 178 (4%) | 26,037 (38%) | 710 (17%) |
| O1 | Optimize Tries to reduce code size and execution time. |
4473 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 22,290 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| O2 | Optimize even more Performs nearly all supported optimizations that do not involve a space-speed trade-off. Increases both compilation time and the performance of the generated code. |
4422 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 21,993 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| O3 | Optimize yet more. O3 turns on all optimizations specified by O2 and also turns on the inline-functions option. |
4485 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 22,176 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| Os | Optimize for size. Os enables all O2 optimizations that do not typically increase code size. It also performs further optimizations designed to reduce code size. |
4356 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 21,885 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
Software Architecture
- Refer to: here
Programming Tips
- Description on developing drivers with POSIX API
Bootloader Development
- Description on concepts and development on bootloader
USB-RS232 Bridge
- As USB ports are becoming more and more common, COM ports and Parallel ports may be redundant in the next few years. This section explore the possibilities of programming the target board through a USB port.
- There are two options:
- Use an external USB/RS232 adaptor, the driver will emulate a virtual COM port, such as Prolific and FDTI. Ingenia has tested its bootloader with some USB-232 manufacturers (silabs, FTDI, etc..). However, the programming failed with our Prolific adapter. Application program may use JavaComm API (javax.comm) and/or RXTX to drive the COM port.
- Modified the bootloader program on PC to support USB communication. e.g. using jUSB and JSR-80 (javax.usb). External circuits such as PIC18F4550 and MAX232 are required.
|--User's App.--|-------Device Manager------|-------USB-RS232 Interface------|---dsPIC---|
Option 1:
+-------------+ +----------+ +----------+ +---+ +------------+ +-----+ +--------+
| Application |--| JavaComm |--| Virtual |==|USB|--| FDTI |--|RS232|==| Target |
| Program | | RXTX | | COM Port | +---+ | Circuitary | +-----+ | Board |
+-------------+ +----------+ +----------+ +------------+ +--------+
Option 2:
+-------------+ +--------+ +---+ +------------+ +-----+ +--------+
| Application |----------| JSR-80 |==========|USB|--| PIC18F4550 |--|RS232|==| Target |
| Program | | jUSB | +---+ | MAX232 | +-----+ | Board |
+-------------+ +--------+ +------------+ +--------+
- Currently, when RXTX is incorporated with JavaComm API, operating systems supported include Linux, Windows, Mac OS, Solaris and other operating systems. On the other hand, jUSB and JSR-80 only works for linux.
FDTI Chipset
- FT232RL communicates with PC via USB to provide 1 UART channel.
- Datasheet can be downloaded here.
- Refer to Fig. 11 (Page 19) for Bus Powered Configuration.
- Refer to Fig. 16 (Page 24) for for UART TTL-level Receive [RXD -> 1], Transmit [TXD -> 4], Transmit Enable [CBUS2/TXDEN -> 3]. Omit Receive Enable [CBUS3/PWREN#] and use [CBUS2/TXDEN -> 2]
- Refer to Fig. 15 (Page 23) for LED Configuration: [CBUS0/TXLED#] and [CBUS1/RXLED#]
- Virtual COM Port Drivers can be downloaded here.
Programming the Device
- Description on how to use dsPicProgrammer to download firmware to dspic
Remote Access
- At the moment, local devices (e.g. EEPROM, ADC, DAC, etc.) can only be accessed locally through POSIX functions such as open(), read(), write(), ioctl().
- However, a client may need to access these devices on a remote server. This section reviews the background and gives some ideas on its possible implementation.
Requirements
- A remote file access protocol, to transfer "files" (i.e. device's data) such as:
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Required files are copied from sever to client for manipulation
- Remote Shell (RSH): Required files are copied from sever to client for manipulation
- Network File System (NFS): Required files are manipulated on sever
- An API to access files using a selected protocol, such as:
- lam_rfposix: A POSIX-like remote file service for Local Area Multicomputer
- API employed by VxWorks: VxWorks is a Unix-like real-time operating system, commonly used for embedded systems.
API Reference for VxWorks
- Reference:
- Related Libraies
- netDrv (netDrv.h): an API using FTP or RSH
- nfsDrv (nfsDrv.h): an API using NFS
Conversion to dsPIC33F Devices
- This section discusses the conversion required from dsPIC30F5011 to dsPIC33FJ128GP306.
- Refer to official document dsPIC30F to dsPIC33F Conversion Guidelines (DS70172A).
- Note that this section does not mainly intend to introduce the new functionalities of dsPIC33F devices. It only serves the purpose to summarise the major (if not minimum) changes required to port the setup of dsPIC30 to dsPIC33 devices.
Downloads
| Program | Site | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| JDK | website | Download latest JDK |
| RXTX | website | Download rxtx-2.1-7-bins-r2.zip or later |
| dsPicBootloader | click | Under "dsPicBootloader/", download bl_5011.s or bl_j128gp306.s |
| dsPicProgrammer | click | Under "dsPicProgrammer/", dowload dsPicProgrammer.jar Alternatively, if you want to compile yourself or modify the source code, download all source files under "dsPicProgrammer/" plus RdFileIntelHex.java under "IntelHexPaser/tags/0.02.00/". You should also install RXTX on your local machine as recommended in the readme file. |
| Ingenia's bootloader | website | Download original ingenia's bootloader |
ToDo
- dspic gcc compiler for constant problem
- add chip to stable voltage upon power failure or to detect low voltage, and generate interrupt for dsPic to execute shutdown routine (e.g. save important data to NVM, shutdown ethernet etc.)
- program the bootloader into flash under linux platform