Difference between revisions of "DsPIC30F 5011 Development Board"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Russ hensel (talk | contribs) m (Reverted edits by FreidaSaunders (Talk) to last revision by Russ hensel) |
|||
| Line 191: | Line 191: | ||
| Free | | Free | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | # Full-featured for the first 60 days | + | # Full-featured for the first 60 days. After 60 days, some code optimization functions are disabled. The compiler will continue to function after 60 days, but code size may increase. |
===RTSP: COM Port (Bootloader)=== | ===RTSP: COM Port (Bootloader)=== | ||
Revision as of 04:44, 2 August 2012
This project aims to provide the development tools for building a multi-purpose MCU board. Description is based on Microchip dsPic33FJ256GP506 (was dsPic30F5011), but information provided in this wiki may give useful directions for developing similar embedded systems with different platforms.
Contents
Introduction
Features of dsPic33FJ256GP506
- 3.0 to 3.3 V
- Up to 40 MIPs
- Maximum current sink/source for I/O pins: 4 mA
- 16-bit arithmetics
- DSP Instruction Set
- Dual programming techniques: ICSP and RTSP
- Memory
- 256 KB flash (86K instructions)
- 16 KB RAM (incl. 2 KB DMA RAM)
- No EEPROM
- Communications ports
- UART
- I2C: up to 1 Mbit/s
- SPI
- ADC
- 10-bit A/D, 1.1 Msps
- 12-bit A/D, 500 ksps
- No DAC (PWMs only)
- Pin-to-pin compatible with other dsPICs
| dsPic | *Price US$ |
MIPs | Flash (kB) |
RAM (kB) |
EEPROM (kB) |
I/O | ADC 12-bit |
IC | OC | Motor Ctrl |
Timers | QEI | UART | SPI | I2C | CAN | Codec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33FJ256GP506 | 6.11 | 40 | 256 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP206 | 4.62 | 40 | 128 | 8 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP306 | 4.81 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| 33FJ128GP706 | 5.49 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 33FJ128MC506 | 4.97 | 40 | 128 | 8 | 0 | 53 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 33FJ128MC706 | 5.38 | 40 | 128 | 16 | 0 | 53 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9x16bit 4x32bit |
1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
*For reference only, subject to change
Forums
- Microchip: Official forum by Microchip
- See MPLAB ICD 2, MPLAB IDE, MPLAB C30 Compiler, ASM30, Link30 forum, dsPIC30F Topics, dsPic33 topics
- HI-TECH Software Forum: Discussion on dsPICC, a C compiler developed by HI-TECH
- FreeRTOS Real Time Kernel: Open Discussion and Support on FreeRTOS
- Nabble: MicroControllers - GNUPIC
References
- dsPIC33F
- ICD2 Programmer
- MPLAB
- C30 Compiler
- MPLAB C30 C Compiler User's Guide: Contains commands for using pic30-elf-gcc
- 16-bit Language Tools Libraries: Contains summaries and examples of using DSP libraries, standard C libraries and device libraries
- MPLAB ASM30, MPLAB LINK30 and Utilities User's Guide
Code Examples
Related Development
Programming Methods
- There are 2 programming methods: In-Circuit Serial Programming (ICSP) and Run-Time Self-Programming (RTSP)
- ICSP allows the devices to be programmed after being placed in a circuit board.
- RTSP allows the devices to be programmed when an embedded program is already in operation.
ICSP: External Programmer (ICD2)
- Two types of ICSP are available: ICSP and Enhanced ICSP. Both of them require setting MCLR# to VIHH (9V – 13.25V).
- Standard ICSP
- Use external programmer (e.g. MPLAB® ICD 2, MPLAB® PM3 or PRO MATE® II) only.
- Required low-level programming to erase, program and verify the chip.
- Slower, because codes are serially executed.
- Enhanced ICSP
- Use external programmer and Programming Executive (PE).
- PE is stored in the on-chip memory.
- PE allows faster programming.
- PE can be downloaded to the chip by external programmer using the standard ICSP method.
- PE contains a small command set to erase, program and verify the chip, avoiding the need of low-level programming.
Hardware Interface
| Pin Label | Function | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| MCLR# | Programming Enable | 7 |
| VDD | Power Supply | 10, 26, 38, 57 |
| VSS | Ground | 9, 25, 41, 56 |
| PGC | Serial Clock | 17 |
| PGD | Serial Data | 18 |
| Product Name | Interface with PC | Interface with Device | *Price (US) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPLAB® ICD 2 | USB or RS232 | 6-PIN RJ-12 connector | $159.99 | - |
| Clone Microchip ICD2 (Now Using) | USB | 6-pin flat cables | $52.35 | Do not work with new MPLAB versions (works for 7.50), communication to MPLAB may sometime hang (see manual) |
*For reference only (exclude shipping), subject to change
| Source | Schematic | PIC16F877A Bootloader |
|---|---|---|
| Patrick Touzet | Yes | HEX |
| Nebadje | Yes | Zip |
Software Interface
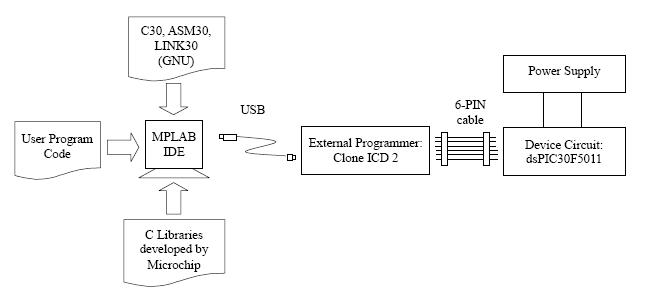
- The program can be written and compiled in an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) using either Assembly or C. The complied codes are then loaded to the device through the external programmer.
| Product Name | Features | OS | Price (US$) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPLAB® IDE | Assembler Only | Windows | Free |
| MPLAB® C30 | Assembler and C-Compiler | Windows | $895.00 (Free student version1) |
| Piklab | Assembler and C-Compiler | Linux | Free |
- Full-featured for the first 60 days. After 60 days, some code optimization functions are disabled. The compiler will continue to function after 60 days, but code size may increase.
RTSP: COM Port (Bootloader)
- RTSP works in normal voltage (MCLR# no need to raise to VIHH).
- No literature has mentioned the incorporation of Programming Executive (PE). Presumably, since Enhanced ICSP needs to set MCLR# to VIHH, RTSP cannot use PE.
- Refer to bootloader section.
Development Environment
Windows
- C-Compiler, Assembler and Linker are under GNU license.
- MPLAB C30 C Compiler (*.c -> *.s)
- MPLAB ASM30 Assembler (*.s -> *.o)
- MPLAB LINK30 Linker (*.o -> *.bin)
- PA optimizer, simulator, runtime libraries, header files, include files, and linker scripts are not covered by GNU. Reference is here.
- Microchip has integrated ASM30, LINK30, assembly header files, linker scripts in MPLAB IDE, which is free for download.
- MPLAB C30 costs US$895. A 60-day free student version is also available. After 60-days, the optimizer is automatically disabled, while other tools can still function properly.
- C-libraries contained in C30 includes (Refer to 16-Bit Language Tools Libraries from Microchip).
| Library | Directory (\\Microchip\MPLAB C30) |
Major functions |
|---|---|---|
| DSP Library (e.g. libdsp-coff.a) |
\lib \src\dsp \support\h |
Vector, Matrix, Filter, etc. |
| 16-Bit Peripheral Libraries | \lib \src\peripheral \support\h |
ADC12, IOPort, UART, I2C, etc. |
| Standard C Libraries (e.g. libc-coff.a, libm-coff.a, libpic-coff.a) |
\lib \src\libm \include |
stdio.h, time.h, float.h, math.h, |
| MPLAB C30 Built-in Functions | none | _buildin_addab, _buildin_add, _buildinmpy, etc |
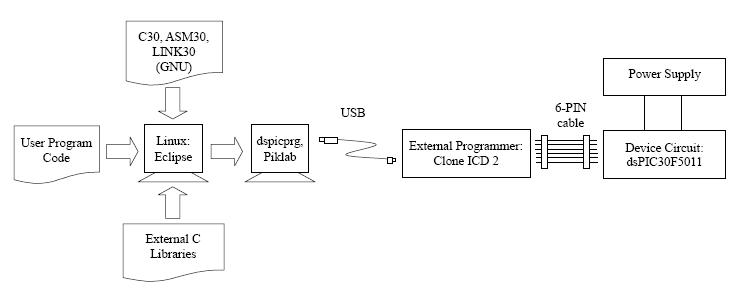
Linux
- C Compiler, Assembler and Linker are under GNU license.
- The code can be downloaded from Microchip at here.
- Current MPLAB ASM30 Assembler: v2.04
- Current MPLAB C30 Compiler: v2.04
- Important Note: Only the compiler is free. The header files and library are owned by Microchip.
| Toolchain Source | Instruction | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| v2.00 | Download pic30-gcc-2.00-1.i386.rpm and pic30-binutils-2.00-1.i386.rpm. Convert to deb files. |
Stable Now using |
| v2.05 | Reference to example below, but use 2.05 files | Can compile Stable but not heavily tested |
| v3.01 | Follow example below | Can compile Unstable (sometime produce segmentation fault) |
| v3.10 | Reference to example below, but use 3.10 files | Cannot compile yet (segmentation fault) |
Conversion Example
- Pre-install these packages: dpkg-dev, debhelper, bison, flex, sysutils, gcc-3.3, fakeroot
- cmd: sudo apt-get install dpkg-dev debhelper bison flex sysutils gcc-3.3 fakeroot
- Download and unzip template: pic30-3.01.tar.bz2
- Download assembler: mplabalc30v3_01_A.tar.gz. Save under /pic30-3.01/pic30-binutils-3.01/upstream/
- Download c-compiler: mplabc30v3_01_A.tgz. Save under /pic30-3.01/pic30-gcc-3.01/upstream/
- Install MPLAB_C30_v3_01-StudentEdition under Windows
- Copy directories /include, /lib, /support, and /bin/c30_device.info to pic30-3.01/pic30-support-3.01/upstream/
- Pack pic30-binutils into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-binutils-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- Install pic30-binutils_3.01-1_i386.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-binutils_3.01-1_i386.deb
- Pack pic30-gcc-3.01 into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-gcc-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- Install pic30-gcc_3.01-1_i386.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-gcc_3.01-1_i386.deb
- Pack support files into deb file
- goto /pic30-3.01/pic30-support-3.01/
- type cmd: dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b
- Install pic30-support_3.01-1_all.deb
- type cmd: sudo dpkg -i pic30-support_3.01-1_all.deb
- After installation, locations of
- C-Header (*.h): /usr/pic30-elf/include
- Libraries (*.a): /usr/pic30-elf/lib
- Assembly header (*.inc): /usr/share/pic30-support/inc
- Linkerscript (*.gld): /usr/share/pic30-support/gld
Burning Program Codes to Target Board
- Use 'dspicprg and dspicdmp' utilities developed by Homer Reid to burn hex code (*.hex) to devices. See Reference here. Through serial port only?
- Use Piklab IDE. Details on file format not known.
- Use MPLAB IDE to burn hex code (*.hex) to devices.
Code Optimization
- Below is a comparsion between different optimization levels for the project including drivers for 2 projects.
| Optimization | Description | Project 1 Code Size (byte) |
Project 1 Data Usage (byte) |
Project 2 Code Size (byte) |
Project 2 Data Usage (byte) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O0 | No optimization Fastest Compilation |
6222 (9%) | 178 (4%) | 26,037 (38%) | 710 (17%) |
| O1 | Optimize Tries to reduce code size and execution time. |
4473 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 22,290 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| O2 | Optimize even more Performs nearly all supported optimizations that do not involve a space-speed trade-off. Increases both compilation time and the performance of the generated code. |
4422 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 21,993 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| O3 | Optimize yet more. O3 turns on all optimizations specified by O2 and also turns on the inline-functions option. |
4485 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 22,176 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
| Os | Optimize for size. Os enables all O2 optimizations that do not typically increase code size. It also performs further optimizations designed to reduce code size. |
4356 (6%) | 178 (4%) | 21,885 (32%) | 710 (17%) |
Driver Development
- Description on developing drivers with POSIX API
Bootloader Development
- Description on concepts and development on bootloader
- Description on dsPicProgrammer to download firmware via bootloader
Programming the Device
- Description on how to use dsPicProgrammer to download firmware to dspic