Difference between revisions of "Motor driver"
(+ VNH3SP30) |
(yet another motor driver, etc.) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* DC motor controller ("brushed") | * DC motor controller ("brushed") | ||
* AC motor controller ("brushless") | * AC motor controller ("brushless") | ||
| + | * BLDC motor controller ("brushless DC"), often called an "ESC" | ||
* ... (todo: fill in the other kinds) ... | * ... (todo: fill in the other kinds) ... | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
A DC motor controller that is 'reversible' generally uses an 'H bridge'. This 'H-bridge' uses four output drivers in a configuration that resembles an H where the load is the cross bar in the middle. The lines on either side of the load (the downward strokes in the H) represent a series connection of a pull-up driver and a pull-down driver. This allows each terminal of the load to be connected to either the positive supply rail, or the negative supply rail. This allows a positive, negative or zero voltage difference across the load. This load voltage is then utilized to provide the desired control required of the motor. The various combinations can give a 'forwards' torque on a DC motor, a 'backwards' torque on the same motor, can allow the motor to free-wheel (without any applied torque) or can provide a locking of the motor such that it resists any attempt to rotate it. | A DC motor controller that is 'reversible' generally uses an 'H bridge'. This 'H-bridge' uses four output drivers in a configuration that resembles an H where the load is the cross bar in the middle. The lines on either side of the load (the downward strokes in the H) represent a series connection of a pull-up driver and a pull-down driver. This allows each terminal of the load to be connected to either the positive supply rail, or the negative supply rail. This allows a positive, negative or zero voltage difference across the load. This load voltage is then utilized to provide the desired control required of the motor. The various combinations can give a 'forwards' torque on a DC motor, a 'backwards' torque on the same motor, can allow the motor to free-wheel (without any applied torque) or can provide a locking of the motor such that it resists any attempt to rotate it. | ||
| − | A single phase AC motor is generally driven in the same way as a DC motor, however instead of operating the motor drive as a constant DC voltage (in either the 'forward' or 'reverse' direction) the AC motor is driven by an approximation to a sinewave. This approximation is created using the H bridge and driving it with a PWM input such that both the positive and negative voltage periods are the same. This is normally achieved either using a sawtooth waveform compared against a sine wave reference, or is done using a lookup table in a microcontroller. | + | A single phase AC motor is generally driven in the same way as a DC motor, however instead of operating the motor drive as a constant DC voltage (in either the 'forward' or 'reverse' direction) the AC motor is driven by an approximation to a sinewave. This approximation is created using the H bridge and driving it with a PWM input <s>such that both the positive and negative voltage periods are the same</s>. This is normally achieved either using a sawtooth waveform compared against a sine wave reference, or is done using a lookup table in a microcontroller. |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
((fill in more details here...)) | ((fill in more details here...)) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == BLDC == | ||
| + | |||
| + | It appears that most modern small electric aircraft, such as [[multi-rotor]] helicopters, use so-called [[motors#Brushless_Motors | "brushless DC motors"]], each one driven by its own "BLDC ESC". (These are easily recognized -- BLDC motors have exactly 3 equally-fat wires that go into them, which come from the BLDC ESC -- as opposed to most electric aircraft a few years ago, which used brushed DC motors with exactly 2 equally-fat wires). | ||
| + | |||
| + | While it is probably not cost-effective to build your own BLDC motor or BLDC ESC, many of us are insatiably curious about what goes on inside these things, and so build one anyway: | ||
| + | * "Proposal for a high-speed serial (spi/i2c) arduino-based ESC for quadrotor/[[multi-rotor]] projects": designed specifically for academic research in stability and controls analysis of quadcopters. The goals are apparently (a) open-source and easy to reprogram, so other academics can replicate the experiments and make improvements, (b) low-latency quick response for (hopefully) better quadcopter stability, (c) lower cost than an Open-BLDC.[http://diydrones.com/forum/topics/proposal-for-a-highspeed] | ||
| + | * Open-BLDC Project wiki: "a completely Open-Source BrushLess Direct Current motor controller also known as Electronic Speed Controller (ESC)." "Open-BLDC has ... many additional sensors to make Vector control possible. The goal is also to make the best possible controller and not the smallest or cheapest." http://open-bldc.org/ | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/brushless_DC_electric_motor Wikipedia: brushless DC electric motor] | ||
| + | * [http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc8012.pdf Atmel AVR444: Sensorless control of 3-phase brushless DC motors] using ATmega48 (also works without change for ATmega88 and ATmega168). Assumes you've already read [http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc2596.pdf Atmel AVR443: Sensor-based control of three phase Brushless DC motor] | ||
| + | * [http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc8138.pdf AVR194: Brushless DC Motor Control using ATmega32M1]: BLDC motor control application using Hall effect position sensors to control commutation sequence. | ||
| + | * MikroKopter brushless motor controller: was designed to give lower latency than off-the-shelf PWM ESCs.[http://www.mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/BrushlessCtrl] | ||
| + | * OpenServo Brushless DC Servo: "The thing that will make our board different from other ESC's is that we are closing the feedback loop with a ... outside position reference." [http://www.openservo.com/forums/viewtopic.php?t=972] | ||
| + | * the [http://blog.spingarage.com/reintroducing-the-froboard-better-and-more-fr FroBoard design] (brushless DC motor control) seems to be open hardware. | ||
== noise control == | == noise control == | ||
| Line 99: | Line 115: | ||
A random collection of semi-related links in no particular order (please prune out the irrelevant ones): | A random collection of semi-related links in no particular order (please prune out the irrelevant ones): | ||
| − | + | * [https://hackaday.io/project/7841-mongoosedc-high-current-motor-driver "MongooseDC : High Current DC Motor Driver"] based around the [http://www.st.com/web/catalog/tools/FM116/SC1041/PF259612 ST Micro VNH5019] which is rated to deliver a continuous 12 A per channel. | |
*[http://www.imagesco.com/articles/picstepper/06.html The UCN 5804 Stepper Motor IC] | *[http://www.imagesco.com/articles/picstepper/06.html The UCN 5804 Stepper Motor IC] | ||
*[http://www.wegatech.com/motor_controller.html Motor controller design]: Custom make motor controller. | *[http://www.wegatech.com/motor_controller.html Motor controller design]: Custom make motor controller. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 122: | ||
* [http://www.robotpower.com/products/osmc_info.html Open Source Motor Control (OSMC)]: The OSMC is a high-power H-bridge circuit designed to control permanent magnet DC motors. It was designed expressly as a motor control for robot combat. Supply voltage: 13V to 50V (36V max battery rating). Output Current (continuous): 160A. Uses 4 MOSFETS (IRFB3207) in each leg of the H bridge, for a total of 16. Bridge Driver: Intersil HIP4081A | * [http://www.robotpower.com/products/osmc_info.html Open Source Motor Control (OSMC)]: The OSMC is a high-power H-bridge circuit designed to control permanent magnet DC motors. It was designed expressly as a motor control for robot combat. Supply voltage: 13V to 50V (36V max battery rating). Output Current (continuous): 160A. Uses 4 MOSFETS (IRFB3207) in each leg of the H bridge, for a total of 16. Bridge Driver: Intersil HIP4081A | ||
* [http://reprap.org/wiki/StepperMotor RepRap: Stepper Motor] lists some stepper motors and stepper motor drivers, including: | * [http://reprap.org/wiki/StepperMotor RepRap: Stepper Motor] lists some stepper motors and stepper motor drivers, including: | ||
| − | * [http://reprap.org/wiki/Stepper_Motor_Driver_2_3 RepRap stepper motor driver] is based around the Allegro A3982 bipolar Stepper Motor Driver with Translator (up to 35 V and up to ±2 A). Like all the RepRap electronics, it is open-source and available on the [http://sourceforge.net/projects/reprap/files/Electronics/ Sourceforge RepRap project files]. You can buy the fully assembled board from (among other places) [http://store.makerbot.com/electronics/assembled-electronics/stepper-driver-v2-3-fully-assembled.html MakerBot Industries] | + | ** [http://reprap.org/wiki/Stepper_Motor_Driver_2_3 RepRap stepper motor driver] is based around the Allegro A3982 bipolar Stepper Motor Driver with Translator (up to 35 V and up to ±2 A). Like all the RepRap electronics, it is open-source and available on the [http://sourceforge.net/projects/reprap/files/Electronics/ Sourceforge RepRap project files]. You can buy the fully assembled board from (among other places) [http://store.makerbot.com/electronics/assembled-electronics/stepper-driver-v2-3-fully-assembled.html MakerBot Industries] |
| − | * [http://forums.reprap.org/read.php?13,5128 Reprap: Arduino] has a long side-thread on various motor driver chips. | + | ** [http://forums.reprap.org/read.php?13,5128 Reprap: Arduino] has a long side-thread on various motor driver chips. |
| − | * [http://www.rrrf.org/2009/04/02/kit-available-stepper-motor-driver-v23/ this RepRap Stepper Motor Driver] was developed by the RRRF as an open source stepper driver. If you are interested in manufacturing/selling the boards, please feel free to do so. | + | ** [http://www.rrrf.org/2009/04/02/kit-available-stepper-motor-driver-v23/ this RepRap Stepper Motor Driver] was developed by the RRRF as an open source stepper driver. If you are interested in manufacturing/selling the boards, please feel free to do so. |
| Line 202: | Line 218: | ||
=== further reading === | === further reading === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Driving Large Loads with the Arduino]] | ||
* [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Robotics/Components/Actuation_Devices/Motors Wikibooks: Robotics motors] | * [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Robotics/Components/Actuation_Devices/Motors Wikibooks: Robotics motors] | ||
| Line 216: | Line 234: | ||
* "you get best microstepping response from motors when the voltage of the power supply is from 1.3 to 5 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor. Your highest speeds are attained in the range of 3 to 8 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor."[http://www.stepperboard.com/UCC30xxCurrentRequirements.htm] | * "you get best microstepping response from motors when the voltage of the power supply is from 1.3 to 5 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor. Your highest speeds are attained in the range of 3 to 8 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor."[http://www.stepperboard.com/UCC30xxCurrentRequirements.htm] | ||
* LMD18200 LMD18201: 3 A, 55 V H-bridge, including 4 MOSFETs, each with a protection diode. The LMD18200 is identical to the LMD18201 except for current sensing: If you want to measure the current through the LMD18201, you must use a shunt (current sense resistor) (0.1 Ω or less), which subtracts from the available voltage drive to the motor. If you want to measure the current through the LMD18200, you use a (much larger) resistor connected to a separate current sense pin. (Is this a current mirror?). However, if you merely want to turn off all the transistors when an output short occurs or a locked-rotor occurs, both devices automatically do that through their thermal overload protection, with no current sense resistor necessary. digital inputs: direction/brake/PWM; digital output: thermal warning flag. | * LMD18200 LMD18201: 3 A, 55 V H-bridge, including 4 MOSFETs, each with a protection diode. The LMD18200 is identical to the LMD18201 except for current sensing: If you want to measure the current through the LMD18201, you must use a shunt (current sense resistor) (0.1 Ω or less), which subtracts from the available voltage drive to the motor. If you want to measure the current through the LMD18200, you use a (much larger) resistor connected to a separate current sense pin. (Is this a current mirror?). However, if you merely want to turn off all the transistors when an output short occurs or a locked-rotor occurs, both devices automatically do that through their thermal overload protection, with no current sense resistor necessary. digital inputs: direction/brake/PWM; digital output: thermal warning flag. | ||
| − | + | * Jose I Quinones has posted schematics for several open hardware motor driver designs online: a [http://ebldc.com/ robotics blog], a [http://robot-talk.com/ robot discussion forum] discussing some of the finer point of motor driver design, and [http://www.avayanelectronics.com/Products/products.html motor drivers]. | |
---- | ---- | ||
[[Category:Projects]] | [[Category:Projects]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:46, 25 September 2015
Contents
kinds of motor drivers
There are many kinds of motor drivers, each one specialized to drive its own type of motors:
- servo motor controller
- stepper motor controller
- DC motor controller ("brushed")
- AC motor controller ("brushless")
- BLDC motor controller ("brushless DC"), often called an "ESC"
- ... (todo: fill in the other kinds) ...
In all cases, we have an electric motor that has wires coming out of it. At any one instant, the motor controller connects each wire to either the Hi voltage on the + side of the battery, or to the Lo voltage on the - side of the battery, or neither. When we tell the motor controller to make the motor go "forwards" or "backwards" or "fast" or "slow", the motor controller changes which wire is connected to which end of the battery (or not connected at all). Some motor controllers switch the connections thousands of times per second in some modes.
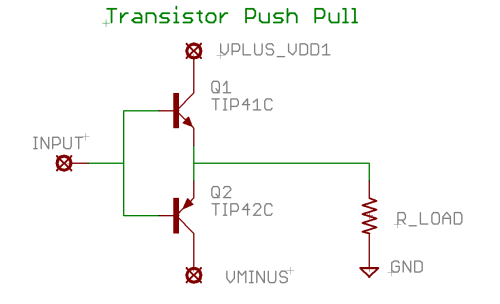
A DC motor controller that is 'reversible' generally uses an 'H bridge'. This 'H-bridge' uses four output drivers in a configuration that resembles an H where the load is the cross bar in the middle. The lines on either side of the load (the downward strokes in the H) represent a series connection of a pull-up driver and a pull-down driver. This allows each terminal of the load to be connected to either the positive supply rail, or the negative supply rail. This allows a positive, negative or zero voltage difference across the load. This load voltage is then utilized to provide the desired control required of the motor. The various combinations can give a 'forwards' torque on a DC motor, a 'backwards' torque on the same motor, can allow the motor to free-wheel (without any applied torque) or can provide a locking of the motor such that it resists any attempt to rotate it.
A single phase AC motor is generally driven in the same way as a DC motor, however instead of operating the motor drive as a constant DC voltage (in either the 'forward' or 'reverse' direction) the AC motor is driven by an approximation to a sinewave. This approximation is created using the H bridge and driving it with a PWM input such that both the positive and negative voltage periods are the same. This is normally achieved either using a sawtooth waveform compared against a sine wave reference, or is done using a lookup table in a microcontroller.
+Vhigh +Vhigh
| |
...-o[pFET pFET]o-...
| |
+--(motor)--+
| |
...-|[nFET nFET]|-...
| |
GND GND
H bridge built from 2 nFETs and 2 pFETs.
A similar method is used to drive multiphase (3-phase) AC motors, however instead of just using an H bridge, only a half H bridge is used per phase (3 half-bridges). Each phases half bridge is then driven in the same manner as for the single phase motor, with a phase difference between the phases as appropriate.
Most stepper motor controllers uses 2 independent H bridges (4 half-bridges) for the 2 independent coils of a stepper motor. Each possible state (one bridge driving current one way, the other way, or free-floating) of both bridges gives 4 "full steps", 4 "half-steps" between the full steps. The "microstepping" motor controllers use PWM to gradually change in a sine-wave-like manner from adjacent full-steps and half-steps.
((fill in more details here...))
BLDC
It appears that most modern small electric aircraft, such as multi-rotor helicopters, use so-called "brushless DC motors", each one driven by its own "BLDC ESC". (These are easily recognized -- BLDC motors have exactly 3 equally-fat wires that go into them, which come from the BLDC ESC -- as opposed to most electric aircraft a few years ago, which used brushed DC motors with exactly 2 equally-fat wires).
While it is probably not cost-effective to build your own BLDC motor or BLDC ESC, many of us are insatiably curious about what goes on inside these things, and so build one anyway:
- "Proposal for a high-speed serial (spi/i2c) arduino-based ESC for quadrotor/multi-rotor projects": designed specifically for academic research in stability and controls analysis of quadcopters. The goals are apparently (a) open-source and easy to reprogram, so other academics can replicate the experiments and make improvements, (b) low-latency quick response for (hopefully) better quadcopter stability, (c) lower cost than an Open-BLDC.[1]
- Open-BLDC Project wiki: "a completely Open-Source BrushLess Direct Current motor controller also known as Electronic Speed Controller (ESC)." "Open-BLDC has ... many additional sensors to make Vector control possible. The goal is also to make the best possible controller and not the smallest or cheapest." http://open-bldc.org/
- Wikipedia: brushless DC electric motor
- Atmel AVR444: Sensorless control of 3-phase brushless DC motors using ATmega48 (also works without change for ATmega88 and ATmega168). Assumes you've already read Atmel AVR443: Sensor-based control of three phase Brushless DC motor
- AVR194: Brushless DC Motor Control using ATmega32M1: BLDC motor control application using Hall effect position sensors to control commutation sequence.
- MikroKopter brushless motor controller: was designed to give lower latency than off-the-shelf PWM ESCs.[2]
- OpenServo Brushless DC Servo: "The thing that will make our board different from other ESC's is that we are closing the feedback loop with a ... outside position reference." [3]
- the FroBoard design (brushless DC motor control) seems to be open hardware.
noise control
Many motors make sparks when the brushes make or break contact. This causes lots of electrical noise ("brush noise"). Your TV-watching neighbors won't be happy if you allow this noise to leak out.
Some people fix this by slapping a .1uF cap across the motor leads. (photo of noise-control capacitor on a Open Servo).
"Sparks emit RF energy from DC to daylight as I was once told by an EMC expert." -- HydraRaptor: "DC to daylight". More details: HydraRaptor: "GM3 motor suppressor"
current sense
Often people want to measure the current going through the motor.
See current sense for several different techniques.
tolerance against software bugs
Some motor controller circuits are such that, if the software accidentally sets the "wrong" pins hi or lo, you get a short circuit through the output drivers. This will generally cause a high current to flow, due to the low on state resistance of the output drivers, which may destroy other electronic components before finally blowing the supply fuse.
Other motor controller circuits are such that, if the software accidentally sets the "wrong" pins hi or lo, the worst that could happen is the motor spins the wrong way. These circuits are designed so that, no matter what the inputs, it is impossible to get a short circuit through the output drivers. Between "one branch on" and "the other branch on", there is a minimum "blanking time" which has "both branches off". This guarantees that we never have "both branches on" (short circuit).
Guess which type of design I prefer?
FET driver
What do you put between the CPU output pins and the 4 FETs of the H bridge?
The simplest solution is to use 2 lo-side nFETs and 2 hi-side pFETs, and use a power supply for the motor that has the same voltage as the CPU power supply, and drive the 4 FETs directly using 2 CPU output pins. One of those output pins connects to the gates of the left side and controls whether the left leg of the motor is Hi or Lo. The other output pin connects to the gates of the right side and controls whether the right leg of the motor is Hi or Lo.
But alas, that circuit won't work for any of the following situations:
- you want to run the motor off a much higher voltage -- say 12 V.
- you want to use 4 nFETs (because they are slightly cheaper, and it's simpler to stock one kind of FET rather than 2 kinds) rather than 2 nFETs and 2 pFETs. You need a "nFET high side driver". There are several clever circuits for generating a "Vpp" voltage that is higher than your motor power supply voltage; "Vpp" is needed to turn high-side nFETs completely on.
- you want more isolation between the "noisy" motor power supply and the "quiet" CPU power supply.
- you are driving a large FET with high gate capacitance, and your CPU output pins can't source or sink enough current to turn the FET on and off fast enough.
- You want a hardware-enforced blanking time as alluded to earlier.
There are many "MOSFET driver" chips designed to drive the gate pin of large discrete MOSFET transistors. In no particular order, a few such MOSFET driver chips are: Microchip TC4423A, TC4424A, TC4425A, MCP1407, On Semi ADP3120A, Fairchild FAN73711, etc.
external links
A random collection of semi-related links in no particular order (please prune out the irrelevant ones):
- "MongooseDC : High Current DC Motor Driver" based around the ST Micro VNH5019 which is rated to deliver a continuous 12 A per channel.
- The UCN 5804 Stepper Motor IC
- Motor controller design: Custom make motor controller.
- Avayan Electronics has many bipolar microstepping stepper motor driver boards and DC motor H bridge drive boards (up to 40A continuous). Many (all?) of them are open source. Avayan sells insanely cheap empty PCBs [4] [5].
- AVRSTMD: AVR-Based Microstepping Bipolar Chopper Stepper Motor Driver (STMD). Based on two National Semiconductor LMD18245T 3A, 55V DMOS Full-Bridge Motor driver chips and a Atmel AVR ATMega48. Drives one stepper motor. Optically isolated so you can connect directly to your printer port. Open Source - The schematic, parts list, and software are all freely downloadable. Easily repaired -- removable screw terminals; all parts are through-hole; etc.
- Open Source Motor Control (OSMC): The OSMC is a high-power H-bridge circuit designed to control permanent magnet DC motors. It was designed expressly as a motor control for robot combat. Supply voltage: 13V to 50V (36V max battery rating). Output Current (continuous): 160A. Uses 4 MOSFETS (IRFB3207) in each leg of the H bridge, for a total of 16. Bridge Driver: Intersil HIP4081A
- RepRap: Stepper Motor lists some stepper motors and stepper motor drivers, including:
- RepRap stepper motor driver is based around the Allegro A3982 bipolar Stepper Motor Driver with Translator (up to 35 V and up to ±2 A). Like all the RepRap electronics, it is open-source and available on the Sourceforge RepRap project files. You can buy the fully assembled board from (among other places) MakerBot Industries
- Reprap: Arduino has a long side-thread on various motor driver chips.
- this RepRap Stepper Motor Driver was developed by the RRRF as an open source stepper driver. If you are interested in manufacturing/selling the boards, please feel free to do so.
- GoBox: a group designing motor driver electronics, a charge controller to optimize getting energy from a variety of energy sources (MTTP solar, wind, water, etc.), and related devices. "The designs and programs are released under a Hardware Open Source License."
- the Open Source Motor Controller Project
- LiniStepper $30 each; Open Source! Circuit Diagram, PCB (Board) Layout, and PIC Software all available. Nice photos of the LiniStepper at http://www.piclist.com/techref/io/stepper/linistep/lini_bld.htm .
- "Design of a High Current Bipolar Stepper Motor Driver"
- H-Bridge Fundamentals An in-depth article on the design of Mosfet H-Bridges
- PMinMO.com Open Source circuits and information on stepper motor controllers] -- in particular, "PMinMO: Stepper Driver Information"
- ePanorama ePanorama Motor Control page
- "Electronic Design of DC Motor Drives" has detailed schematics and PCB layout for a system that has a PC send commands through the serial port to a Microchip PICmicro, which does PWM control of 2 H bridges. Each half-bridge uses a IRF9530N (100V 14A pfet plus flyback diode) and a IRF530 (IRF530NPBF: 100V 17A nfet plus flyback diode), driven by a small transistor inverter based on a BD135 npn, for a total of 12 discrete transistors.
- OpenServo wiki -- developing a digital servo motor that accepts "Go to position X" commands and also more complex curves, and returns actual servo position, speed, voltage and power consumption.
- OpenStepper -- geared stepper motor plus driver. microstepping, 2 kg/cm torque, I2C interface, Freescale MPC17529[6] dual H bridge (0.7 A DC, 1.4 A peak, up to 6.8 V, 0.65 mm pitch), ATtiny84 -- firmware is open source, based on OpenServo.
- MOSFETs and MOSFET drivers
L298 quadruple half-bridge driver, aka dual full-bridge driver: pin-compatible with SN754410 and L293 and L293D. They all require external flyback diodes when driving motors (the L293D is apparently the only one with built-in flyback diodes).
- L297 stepper motor controller + L298 dual full-bridge driver: for driving one (4-wire) bipolar stepper motor (2 A); direction and step inputs; half-stepping; on-chip PWM chopper limits current. external diodes are required (preferably Shottky). (Both chips come in through-hole and SMT versions)
- L298 dual full-bridge driver can also be used to drive 2 independent DC motors (2 A each); external diodes are required (preferably Shottky). L293D is similar, but only rated up to 1 A, 36 V.
- Motor Shield - Arduino motor/stepper/servo control: has 2 connections for 5V 'RC' 'hobby' servos; and also 4 H-Bridges: L293D chipset provides 0.6A per bridge (1.2A peak) with thermal shutdown protection, 4.5V to 36V; each L293D can be independently programmed to either drive a unipolar or bipolar stepper motor with full, half, or microstepping -- or else drive two bi-directional DC motors -- so this board can control a maximum of 4 DC motors and 2 RC servomotors.
- SN754410 quadruple half-bridge driver is pin-compatible with the L293. DIP package. 1 A per bridge continuous (2 A peak) with thermal shutdown protection, 4.5 V to 36 V. Requires external flyback diodes (preferably Schottky).
- STMicroelectronics L6506 is designed to work with a L293 or L298 dual bridge drivers to form a constant current drive for the (inductive) stepper motor. This chip senses the current in each load winding (with an external sense resistor); if either winding exceeds the desired current (also programmed with external sense resistors), the L6506 unconditionally turns off that coil. (This chip would presumably fit in-between a microstepping stepper motor controller and the dual bridge chip).
- STMicroelectronics made fully integrated H-bridge motor driver VNH3SP30. It has only one disadvantage: too low frequency (10 kHz max). But its enough for many automotive applications.
- SparkFun sells a long list of motor drivers and servo drivers, including:
- SparkFun: EasyDriver v3 Stepper Motor Driver based on A3967 microstepping driver chip; up to 750mA, 30 V.
- some Pololu motor drivers, some of them up to 13A continuous output current
- a Cana Kit PWM DC motor controller (only in one direction, because it doesn't have a full H bridge); 50A maximum continuous current at 9 to 30V DC (12V DC Recommended); [7]
- the Sparkfun version of an OpenServo [8]
- L6208N stepper motor driver: driving one (4-wire) bipolar stepper motor; up to 2.8 A, 52 V. direction and step inputs. PWM current control; includes internal diodes. over-current and thermal protection. half-stepping. MC3479 stepper motor drive is similar, but only rated up to 350 mA, 16 V.
- Nanotec sells microstepping stepper motor driver chips (the IMT-901, IMT-902, and IMT-903) and assembled stepper motor driver modules.
- NANOTEC - IMT-901[9]: microstepping constant current stepper motor driver. 1.5 A continuous, 2.5 A peak. Up to 40 V. Selectable full step, 1/2 step, 1/4 step, 1/8 step. Requires 4 external flyback diodes (apparently has the other 4 flyback diodes built in?).
- Ardumoto - Motor Driver Shield[10]: has one L298 dual H-bridge and the 8 necessary Schottky diodes; can drive up to 2 amps per channel.
- lots of stepper motor driver chips
- Critical Velocity sells DC motor speed controllers and stepper motor controllers.
- Geckodrive sells DC motor speed controllers and stepper motor controllers.
- PICStep stepper motor driver -- schematic, PCB, parts list, firmware, etc. (based on PIC16F628A)
- AVR2313 stepper motor driver schematic, PCB, parts list, firmware, etc.
- Unipolar Stepper Motor Driver (74194) (uses a SN74LS194 - Bidirectional Universal Shift Register, not a CPU)
- Simple L297/298 Based Stepper Motor Driver
- Galil in motion: motor tutorials -- anything useful here?
- Mesa Electronics sells "motion control cards" including "a single axis 100W smart servo motor controller on a 2"x2" PCB."
- H bridge oscillators (used to drive isolated power transformers, electroluminescent panels, CCFLs, etc.): "DC-AC inverter targets electroluminescent applications" 1997 describes the Sipex SP4425 IC which converts a low input DC voltage ( 1.1 V to 3.0 V ) to a high output H bridge square wave (400 Hz, 150 V typ.) (Is the Sipex SP4425 still being manufactured, or is there some other IC which obsoletes it?). Maxim MAX4990 high-voltage DC-AC converter for driving electroluminescent (EL) lamps: +2.4V to +5.5V input range; up to 250V peak-to-peak output voltage ... many CCFL controllers use a full H bridge ... the Maxim MAX256 has a built-in full H bridge ... the Maxim MAX5069 can be used to build full-bridge switching power supplies ... and some Class D audio amplifiers use full H bridges ...
- A bunch of H bridge motor driver circuits are on the Red Rock Energy web page. They are designed to control the motor that tilts solar panels towards the sun.
- "Motor Drives and Audio Amplifiers" by Dennis L Feucht
- "circuit for changing direction with a DC motor"
- "H-Bridge secrets"
- "Integrating the H-bridge and its controller" by ian 2006
- MotorDriver by Pascal Stang, Procyon Engineering. based on National Semiconductor LMD18200 H-bridge chips ... Up to 50V, 3A continuous, per channel ... "Can connect directly to AVRmini or STK500 with just one or two 10-pin ribbon cables"
- "Motor and Servo Controllers" from RobotGear in Australia
- Total Robots distributes motor controllers from several companies, including motor controllers from Sabertooth up to 18 V, 25 A continuous; and USB-controlled motor controllers from Phidgets up to 15 V, 14 A continuous.
- The Pololu "A4983 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier with Voltage Regulators" operates from 8 – 35 V and can deliver up to 2 A per coil. The driver features adjustable current limiting and five different microstep resolutions. This is the tiniest stepper motor driver I've ever seen.
- "Easy CNC Stepper Motor Drivers"[11] sells a few stepper motor drivers that operate from 12 VDC to 48 VDC; up to 10A motor current capacity per phase. Screw terminal block. Also sells used NEMA 23 stepper motors to go with them.
A3977
Using the A3977 microstepping driver chip from Allegro:
- "Keith’s Stepper Motor Controller Board"
- "A3977 Microstepping Stepper Motor Driver Prototype PCB" / THSTEP25 Microstepping Stepper Motor Driver (sells bare PCB board; schematic on web site)
- "Tero's A3977 stepper driver" (schematics and layout files)
- "PMinMO: A3977 Stepper Driver Board"
- "another A3977-based board." at http://microstepping.com/ .
astronomy
astronomy telescopes use motor drivers:
- scope drive webring: a selection of Websites that display procedures to equip amateur telescopes with homemade computerized drive systems
- "scopedrive" for automating telescopes
robots
Robots use motor drivers.
- Glendale robotics club (Glendale CA)
- "H bridges" by David Cook at the ROBOT ROOM(TM)
- "A Second Generation Speed Controller" by Chuck McManis. Can handle 200 amps continuously. Uses two PIC16F628 chips driving sixteen IRF1010E FETs: "(I like to call it a "two way SMP microkernel with serial cluster interconnect" as that sounds better than "a couple of PICs with their serial ports wired together" :-)"
self-balancing personal transportation systems
- Main Article: vehicle
Self-balancing personal transportation systems use motor drivers:
- Project Emanual: The Almost Self Balancing 2 Wheeled Electric Skateboard (uses a PIC16F73 microcontroller; source code for the balancing algorithm in PIC assembler can be downloaded there)
- The Electric Unicycle
generator
(This doesn't have much to do with motor drivers -- is there a better page for electric power generation tips?)
- performance axial flux discussion group develops axial flux motors and alternators
- Alternator and Generator Comparison for Wind Power
- Windstuffnow discusses DIYS wind power
- Otherpower discusses wind turbine construction, generating electricity from firewood, etc.
further reading
- Wikibooks: Robotics motors
- "Brushed DC Motor Drive Circuits" on the Microchip wiki.
- "Variable Speed Induction Motor Controller" by Richard Wotiz 2007
- Microchip app note AN898: "Determining MOSFET Driver Needs for Motor Drive Applications" includes a section on "MOSFET or IGBT, what’s best for your application?" and some gate driver circuits.
- The Flip-Flop Robot uses the IXDN404 chip as a single-chip H bridge motor driver for 1 small motor.
- the Joystick controlled robot uses a FAN8200 motor driver chip as a single-chip H bridge motor driver to drive 2 small motors.
- Linistepper open source microstepping controller / driver for stepper motors. Has PMinMO standard connections.
- Massmind: motors has links to general information about various kinds of motors and motor controllers
- DIY Sewing Machine Retrofit: Micah mentions "The LMD18200 is an amazingly versatile and robust little chip." -- the LMD18200 has one H bridge (4 MOSFET transistors) on one chip (3A continuous; up to 55V), plus "Thermal warning flag output at 145°C" and "Thermal shutdown (outputs off) at 170°C". (is this better, worse, or simply different from the LMD18245T ?).
- Acroname: "Driving Loads with High Current" discusses relays, transistor H bridges, and RC motor controllers, and a few tips for using them.
- "Stepper Motors and Control: Part III - Current Control of Stepper Motors"[12]
- "you get best microstepping response from motors when the voltage of the power supply is from 1.3 to 5 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor. Your highest speeds are attained in the range of 3 to 8 times the 'nominal' voltage for the motor."[13]
- LMD18200 LMD18201: 3 A, 55 V H-bridge, including 4 MOSFETs, each with a protection diode. The LMD18200 is identical to the LMD18201 except for current sensing: If you want to measure the current through the LMD18201, you must use a shunt (current sense resistor) (0.1 Ω or less), which subtracts from the available voltage drive to the motor. If you want to measure the current through the LMD18200, you use a (much larger) resistor connected to a separate current sense pin. (Is this a current mirror?). However, if you merely want to turn off all the transistors when an output short occurs or a locked-rotor occurs, both devices automatically do that through their thermal overload protection, with no current sense resistor necessary. digital inputs: direction/brake/PWM; digital output: thermal warning flag.
- Jose I Quinones has posted schematics for several open hardware motor driver designs online: a robotics blog, a robot discussion forum discussing some of the finer point of motor driver design, and motor drivers.